Darjeeling is the name of our 2021 Tisane update. While we worked on multiple parts of the system, the focus in this update is on moving beyond the “sliding window” of one sentence. The current edition adds powerful tools to make the system aware of non-textual content, as well as context coming from different messages.
See below short notes on the new features and changes.
Automatic Language Detection
For those working with multiple languages, it is now possible to use the automatic language detection. In addition to the new method, it can be activated in other methods as well; simply specify * as the language code value. If the likely languages are known, specify them the vertical bar-delimited list of the likely language codes, e.g. en|es|ja.
More Subtypes for Abuse
We added more tags to describe the various shades of abuse. In the instances of hate speech (bigotry type), we now detect the protected class being targeted, generating tags like racism, xenophobia, sexism, religion, and more.
Runtime Redefinition: Codewords & More
Redefining concepts & features on the fly became possible thanks to the brand new Long-Term Memory module. From conversations with the law enforcement users, we learned that codewords are a persistent challenge that subverts detection efforts. Tisane now allows redefining what concepts mean; not just adding word for word, but redefining entire families or even categories.
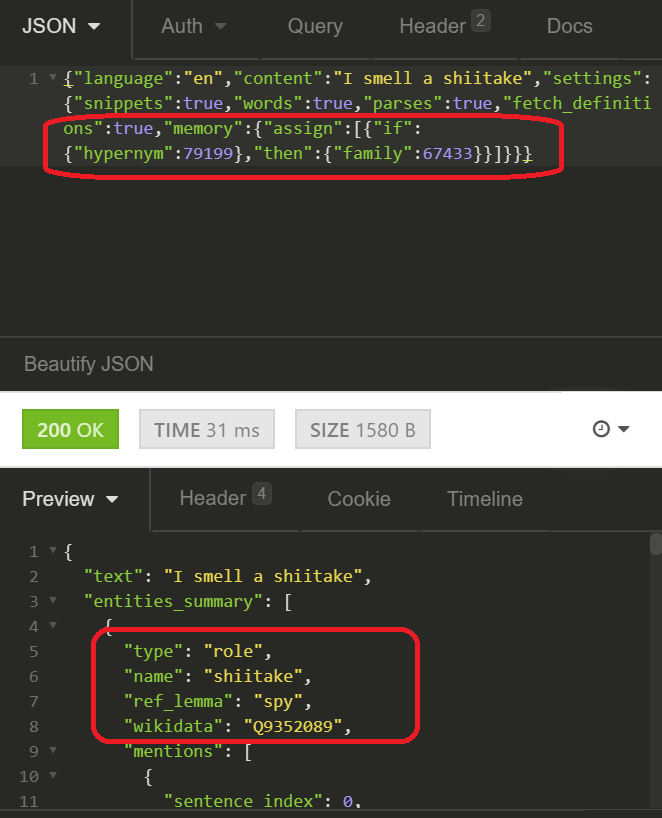
E.g. if someone consistently means spies when mentioning any types of mushrooms (be it champignons, chanterelles, etc.), there is a new structure in the settings that allows redefining it. Upon learning of the hidden meanings, the users then can request the service to interpret some concepts differently, reprocess the text, and detect patterns that were skipped. Contact us to learn more.
The redefinition module allows redefining both meanings and features. For example, we can define that the gender of the speaker or the interlocutor for languages where these pronouns do not have gender, generating translations with the correct gender. We can assign new categories, reflecting subjective opinions (e.g. link a particular political faction to the concept of “unwelcome person” to gauge sentiment). The runtime redefinitions will then work in concert with the pre-built language models.
Nontextual Context Flags
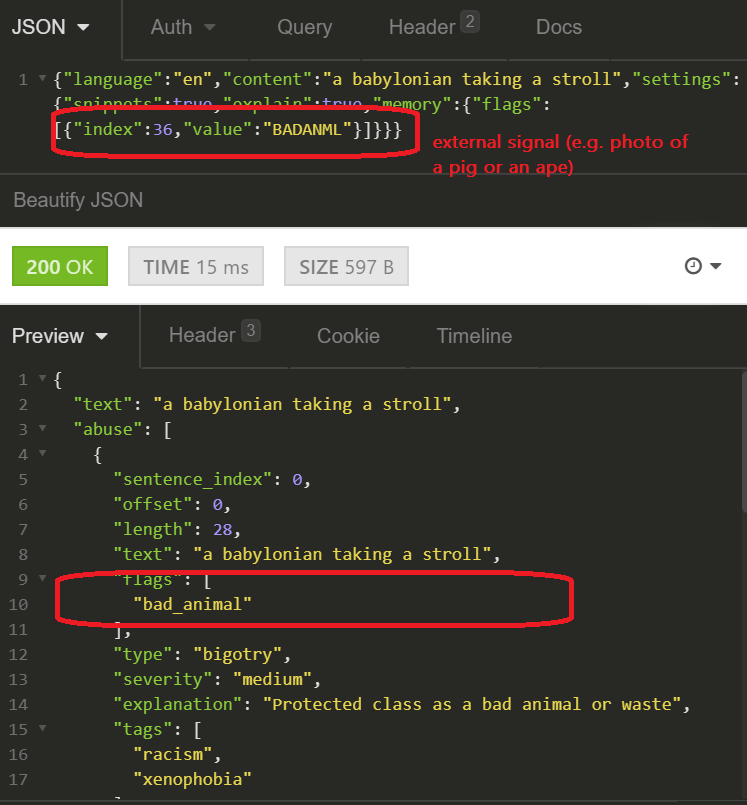
Another use of the Long-Term Memory module is to define non-textual context. For example, if a meme shows a pile of refuse or an animal associated with negative qualities (ape, pig, snake) and the text overlay names a protected class, the text in itself is not offensive. However, the message is undoubtedly is. It is now possible to set a flag for particular types of situations. These flags will provide context, allowing Tisane to detect more.
Multi-step Detection
For the subtle and gradual kind of abuse, the picture is never clear from just one sentence. The offender may require multiple steps to gain confidence of the victim, or spin a long story, each part of which is neutral in isolation.
We now allow issuing alerts only when several flags fire. While Tisane remains stateless, it is possible to port the context and the accumulated knowledge from the previous messages in the conversation to the subsequent messages.
